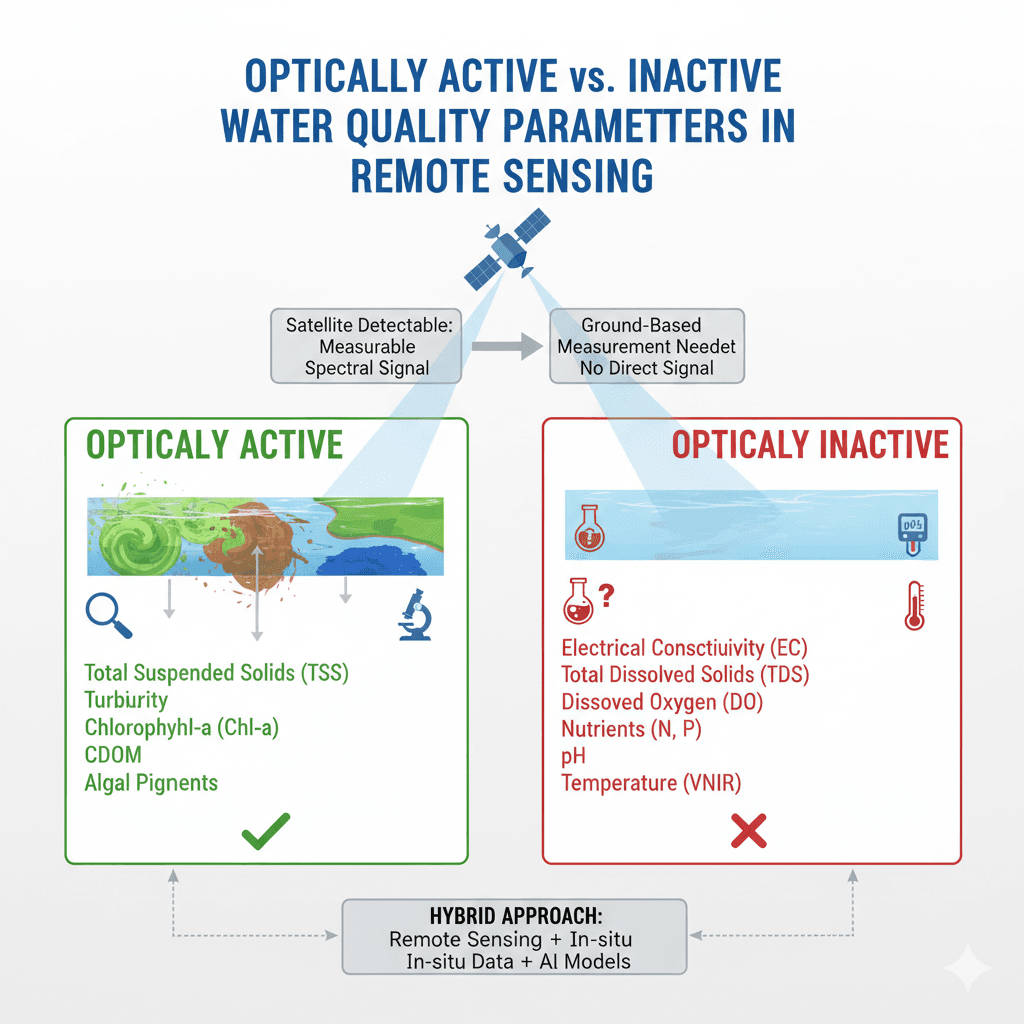
Remote sensing, the art of gathering information about the Earth without physically touching it, is undergoing a dramatic transformation thanks to the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI). This article, based on a comprehensive review adopted from Janga et al 2023 research, explores the exciting intersection of these two fields and its potential to revolutionize Earth sciences.
The Power of Remote Sensing
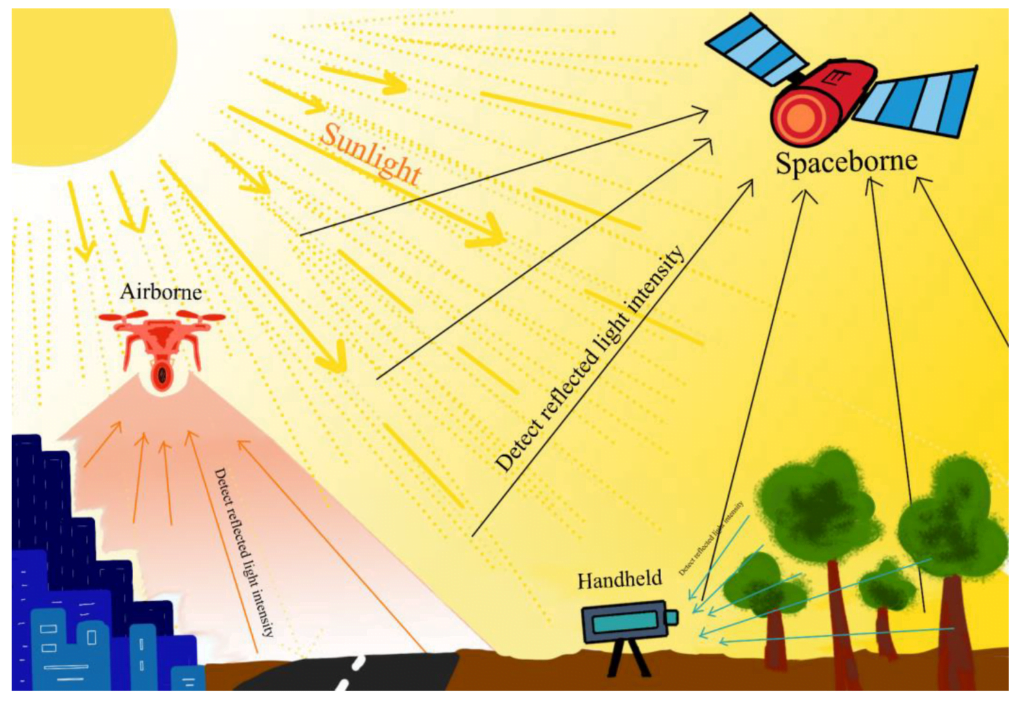
Remote sensing relies on sensors (as shown in below figure) to detect and measure various types of energy, like electromagnetic radiation and acoustic signals, emitted, reflected, or scattered by the Earth’s surface, atmosphere, and even its interior. This data provides invaluable insights into our planet’s health, resources, and changes over time.
The Rise of AI: Unleashing the Potential of Data
AI, particularly deep learning, offers powerful tools for analyzing the massive amounts of data generated by remote sensing. These tools can:
- Extract Meaningful Information: AI algorithms can identify complex patterns, detect subtle changes, and classify objects in remote sensing imagery with remarkable accuracy.
- Automate Processes: AI can automate tasks like image processing, data fusion, and anomaly detection, freeing up scientists to focus on higher-level analysis and interpretation.
- Improve Predictions: AI models can be trained to predict future events, like natural disasters, resource availability, and environmental changes, based on historical data and current observations.
Unlocking the Potential: AI Applications in Remote Sensing
AI is transforming various aspects of remote sensing, leading to groundbreaking applications in:
- Image Classification: AI algorithms can classify land cover types, identify different vegetation, and map urban areas with unprecedented detail.
- Object Detection: AI can detect and locate specific objects, like buildings, vehicles, and even individual trees, in remote sensing imagery.
- Change Detection: AI can monitor changes over time, such as deforestation, urban sprawl, and glacier retreat, providing valuable insights into environmental trends.
- Hyperspectral and Radar Data Analysis: AI can analyze complex hyperspectral and radar data, revealing information about soil composition, crop health, and even underground structures.
- Data Fusion: AI can combine data from multiple sensors to create more comprehensive and accurate representations of the Earth’s surface.
Navigating the Challenges: A Path to Practical AI
While AI holds immense promise for remote sensing, there are challenges to overcome:
- Data Quality and Availability: AI models require large, high-quality datasets for training, which can be expensive and time-consuming to acquire.
- Model Uncertainty and Interpretability: Understanding why AI models make certain predictions is crucial for trust and decision-making, but many models remain “black boxes.”
- Integration with Domain Expertise: AI models need to be developed in collaboration with domain experts to ensure they capture the nuances and complexities of specific applications.
The Future is Bright: Emerging Trends and Solutions
Despite the challenges, progress is being made:
- Advancements in AI Techniques: New algorithms and architectures are being developed to improve the performance, efficiency, and interpretability of AI models for remote sensing.
- Open Data and Collaboration: Initiatives are underway to make remote sensing data more readily available and encourage collaboration among researchers and developers.
- Hybrid Approaches: Combining AI with traditional remote sensing techniques can leverage the strengths of both approaches to create more robust and reliable solutions.
The Impact of AI: Transforming Our World
The integration of AI with remote sensing is poised to transform various fields, including:
- Environmental Monitoring: AI can help track deforestation, pollution, and climate change, enabling us to better understand and mitigate these challenges.
- Resource Management: AI can optimize the use of natural resources, like water, soil, and minerals, ensuring their sustainable use.
- Disaster Response: AI can help predict and respond to natural disasters, like earthquakes, floods, and wildfires, saving lives and minimizing damage.
- Urban Planning: AI can assist in planning and managing cities, optimizing transportation, infrastructure, and resource allocation.
- Precision Agriculture: AI can improve crop yields, reduce pesticide use, and optimize water usage, leading to more efficient and sustainable agricultural practices.